Pigmentary Diseases
The pigment cells or melanocytes are located at the base of the epidermis and produce the melanin. This melanin is responsible for our skin color. There are various skin diseases which can result in generalised or localised hyperpigmentation (increased skin colour), hypopigmentation (reduced skin colour), or achromia (absent skin colour).
Common pigmentary diseases are:
- With Hypopigmentation – Vitiligo, Pityriasis alba, Albinism, idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis, leprosy, etc.
- With Hyperpigmentation – Melasma, Riehl’s melanosis, Lichen planus pigmentosus, post-inflammatory pigmentation, Fixed drug eruption etc
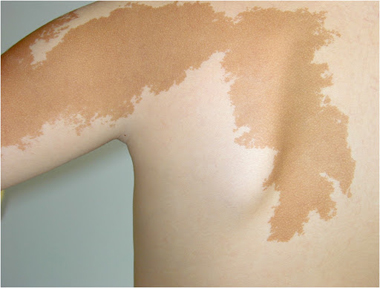
Vitiligo
It is one of the most common pigmentary diseases, also known as leukoderma. It can occur at any age from childhood to old age.
Cause- Vitiligo occurs when pigment-producing cells die or stop functioning. The exact reason why this happens is not known. But there is an important role in genetics. So persons with a family history of vitiligo are at more risk of developing it. It does not spread by touching. And it is not related to eating any food.
It is characterized by the appearance of white patches over the body. Loss of skin colour can affect any part of the body, including the mouth, hair and eyes. The patient may develop only a few patches or may develop the widespread disease, it varies from patient to patient.
Treatment– There is no permanent cure. But with advancement, multiple options are now available for controlling the disease. For a few lesions creams containing topical steroids, tacrolimus, decapeptide etc can be used or localized phototherapy can be used.
For extensive disease phototherapy is 1st line treatment. Other options are oral steroids, methotrexate, cyclosporin, azathioprine etc.
In chronic non-responding cases surgery can be done.
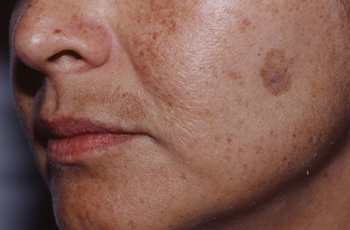
Melasma
It is a very common problem in females, although it can occur in males also. It usually occurs between the 20 – 40 year age group. Many women develop it 1st time during pregnancy, which may or may not fade after delivery.
The brown or grey-brown patches appear most often on the cheeks, forehead, nose and chin.
Causes- Multiple factors are responsible which include female hormones, sun exposure, oral contraceptive intake, genetics etc.
Treatment- Medicines can’t cure it. But It can be improved with help of medicines.
- Don’t self-medicate because it can harm your face
- Sun protection is the most important thing, you have to use sunscreen regularly.
- Certain creams containing chemicals like hydroquinone, azelaic acid, ascorbic acid, tretinoin, kojic acid, vitamin c, niacinamide etc will help in decreasing pigmentation.
- Certain oral medications like tranexamic acid, antioxidants also help in improving pigmentation.
- Chemical peels are very useful in these patients.
- The laser can be used if other therapies fail.
- Another important thing is don’t be afraid of using concealer to hide these blemishes, as these are an important part of the treatment regimen.
